Permission
Permissions
(1) Windows Platform
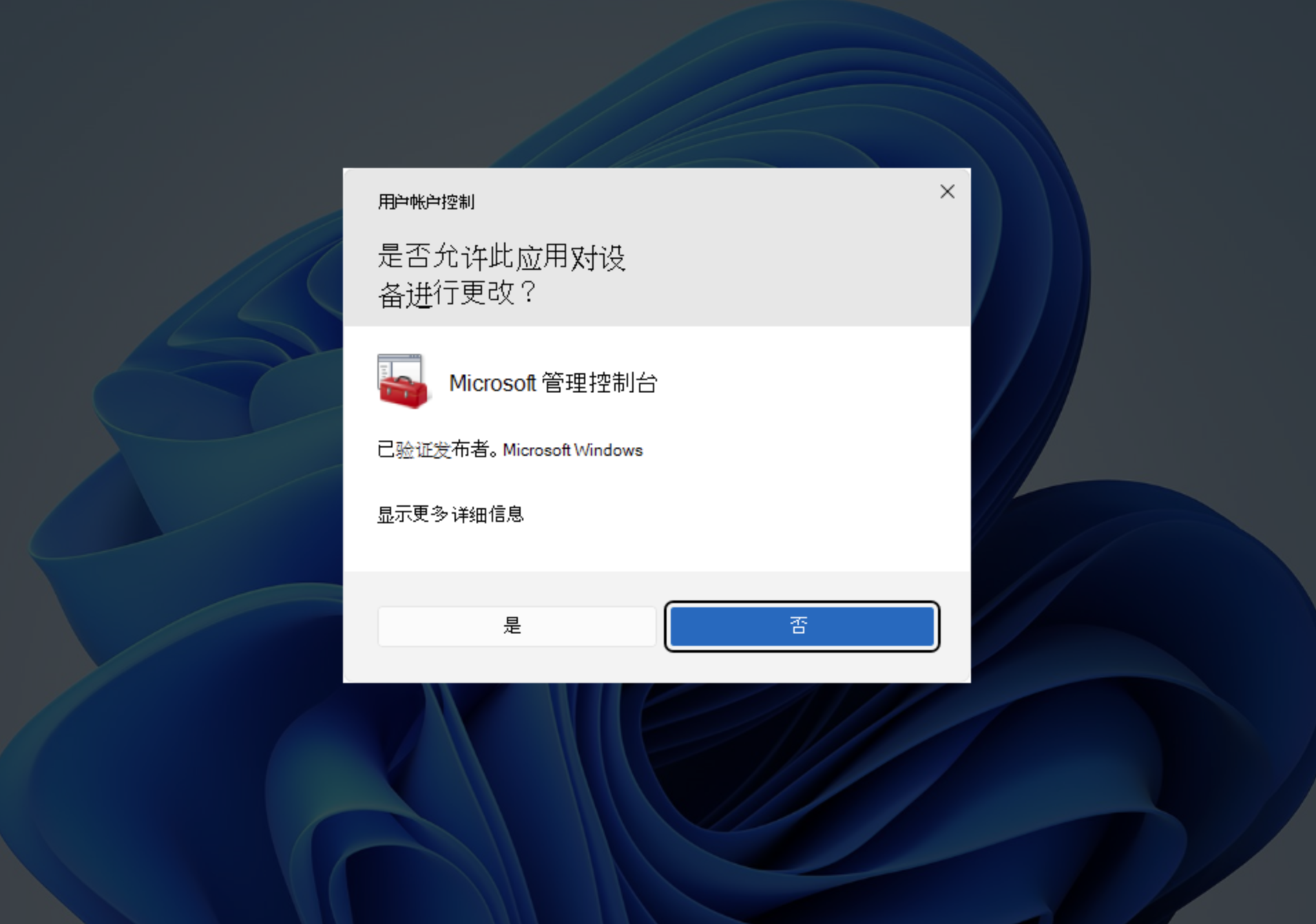
When using GeneralUpdate for automatic updates, you may encounter permission issues if the update directory is on the C drive, especially when replacing files or applying patches. With the introduction of Windows 11, permission management for certain directories on the C drive has become more stringent compared to previous Windows operating systems.
It's important to be aware of which directories might trigger permission issues:
| Name | Directory |
|---|---|
| System Folder | C:\Windows |
| Registry Config | C:\Windows\System32\config |
| Driver Folder | C:\Windows\System32\drivers |
| Program Folder | C:\Program Files and C:\Program Files (x86) |
Recommended directories to avoid permission issues:
| Name | Directory |
|---|---|
| User Data Directory | AppData |
| System Temporary Directory | Temp |
Lowering UAC
The following method is not recommended for use in production environments as it may cause issues for users. If you encounter UAC (User Account Control) prompts or permission/access denied issues during updates, you might consider lowering the UAC control level. This can be done by modifying the registry as follows:
| Registry Name | New Value | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| enableLUA | 0 | 1 |
| ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin | 0 | 5 |
Modify the above registry settings before the update (effective after restarting the computer), and be sure to restore them after the update is complete.
C# code to modify the registry:
using Microsoft.Win32;
public void UpdateRegistry()
{
const string keyName = @"SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System";
using (RegistryKey key = Registry.LocalMachine.OpenSubKey(keyName, true))
{
if (key != null)
{
key.SetValue("EnableLUA", 0, RegistryValueKind.DWord);
key.SetValue("ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin", 0, RegistryValueKind.DWord);
}
}
}
Batch script to modify the registry:
@echo off
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /v EnableLUA /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
REG ADD "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System" /v ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
References: